What is 3D Printing?
3D printing, a revolutionary technology that has transformed manufacturing and design, stands on the cusp of even greater advancements. This article delves into what 3D printing is, its various technologies, applications, current usage in everyday life, and its promising future.
3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, involves creating three-dimensional objects from a digital file by adding material layer by layer. This technology stands in contrast to traditional subtractive manufacturing, where material is removed to create an object. It enables complex designs, reduces material waste, and offers unprecedented flexibility in production.
3D Printing Technologies
Several technologies underpin 3D printing, each suited to different applications. Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM), the most common form, uses a heated nozzle to melt and extrude thermoplastic filaments. Stereolithography (SLA) employs ultraviolet light to cure liquid resin into solid plastic. Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) fuses powder particles using a laser, ideal for creating durable and complex parts. Each technology has its unique advantages, catering to various needs in manufacturing.
Application of 3D Printing
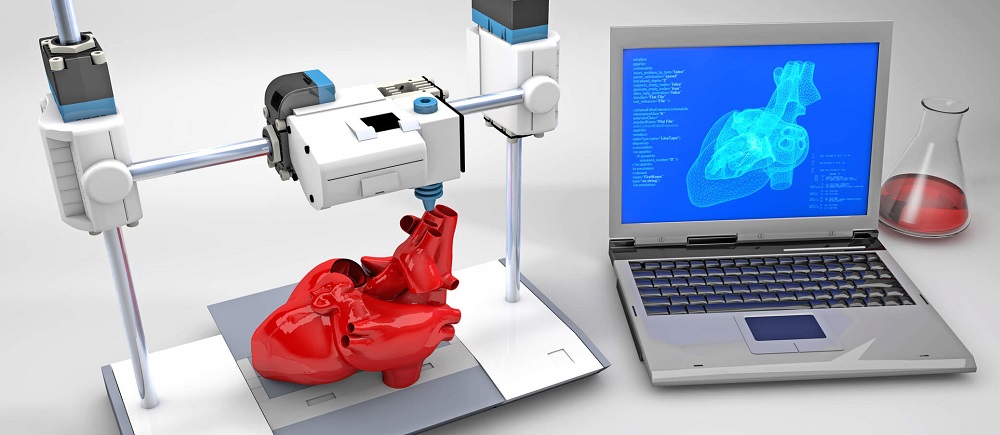
The applications of 3D printing are vast and varied. In healthcare, it’s used for printing prosthetics, dental implants, and even organ tissues. Aerospace and automotive industries leverage it for producing lightweight, strong parts. In the realm of consumer goods, it allows for the customization of products from shoes to eyewear. The construction industry is exploring 3D printing for building houses, promising faster and more cost-effective construction methods.
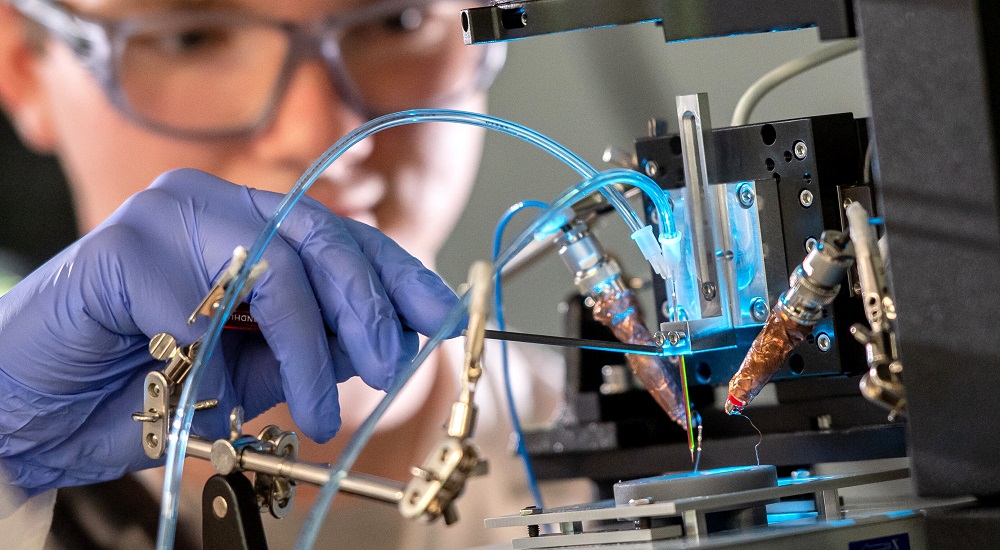

Prospects
The future of 3D printing is incredibly bright. Advances in materials, such as the development of stronger and more versatile filaments, will expand its applications. The integration of AI and machine learning could lead to smarter, more efficient printing processes. Sustainability will also be a key focus, with the potential for 3D printing to use recycled materials, reducing environmental impact.
How is it used today in everyday life?
Today, 3D printing is increasingly becoming a part of everyday life. Consumers can find 3D-printed products ranging from jewelry to home decor. Educational institutions use 3D printers for teaching engineering and design principles. Chips of various denominations are printed for winfest casino. In medicine, custom 3D-printed surgical tools and patient-specific models for surgical planning are becoming more common. Its accessibility continues to grow, with online platforms allowing individuals to design and order 3D-printed items.
Conclusion
3D printing technology is not just a manufacturing tool, it’s a catalyst for innovation and creativity across industries. His ability to quickly and efficiently transform ideas into tangible objects has already had a profound impact, from things as small as gambling chips at Winfest Casino to the use of printing in construction. As it continues to evolve, 3D printing promises to reshape how we create, learn, and think about the physical world.
